Jet Fuel
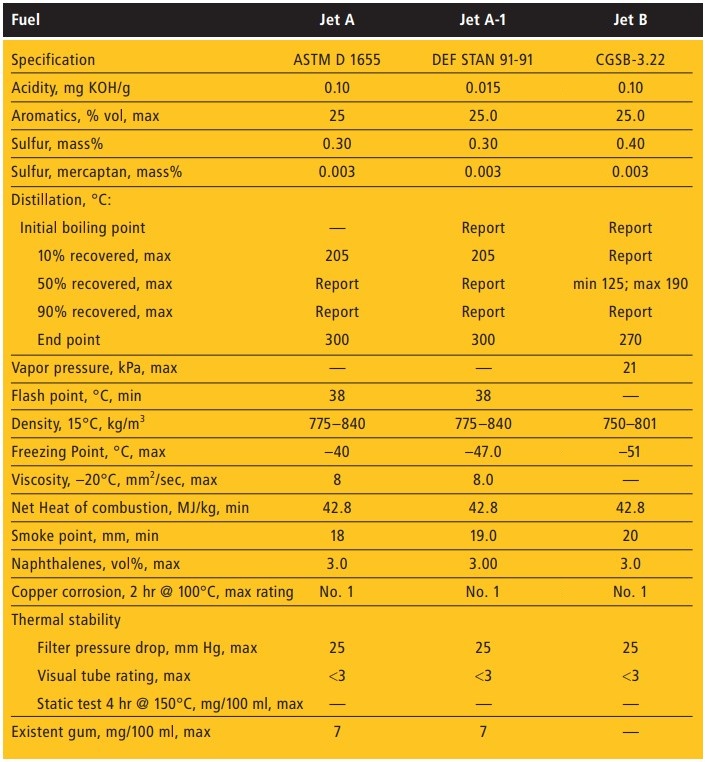
Jet fuel is a type of aviation fuel used in aircraft with gas-turbine engines. It is a refined kerosene-based liquid that is usually clear or straw-colored and smells like kerosene. Jet fuel is denser than gasoline and has a higher flashpoint and lower freezing point, making it safer to use in turbo-jet aircraft. The most commonly used fuels for commercial aviation are Jet A and Jet A-1, which are produced to a standardized international specification. The only other jet fuel commonly used in civilian turbine-engine powered aviation is Jet B, which is used for its enhanced cold-weather performance.


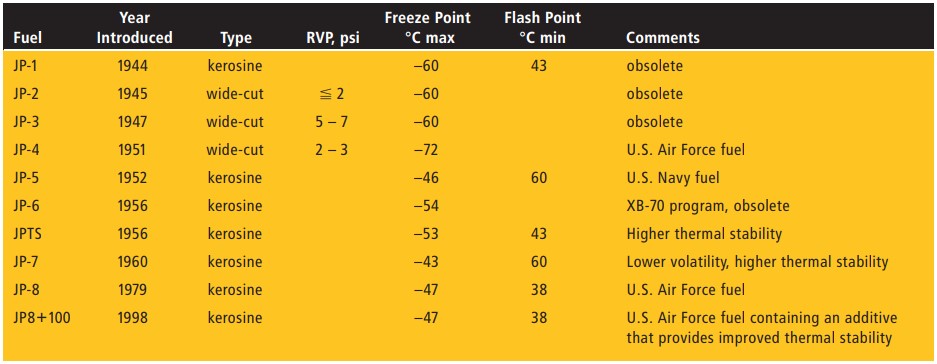
Selected Specification Properties of Jet Fuels
Military Fuels
Military around the world uses a different classification system (known as JP or “Jet Propellant” numbers). The reasons for separate specifications include the operational and logistical differences between the military and civilian systems and the additional demands high-performance jet fighter engines place on the fuel. Some are almost identical to their civilian counterparts and differ only by the amounts of a few additives; Jet A-1 is similar to JP-8, and Jet B is similar to JP-4. There are currently two fuels in widespread use by the U.S. military: JP-5 by the Navy, and JP-8 by the Air Force.
U.S. Military Jet Fuels